
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
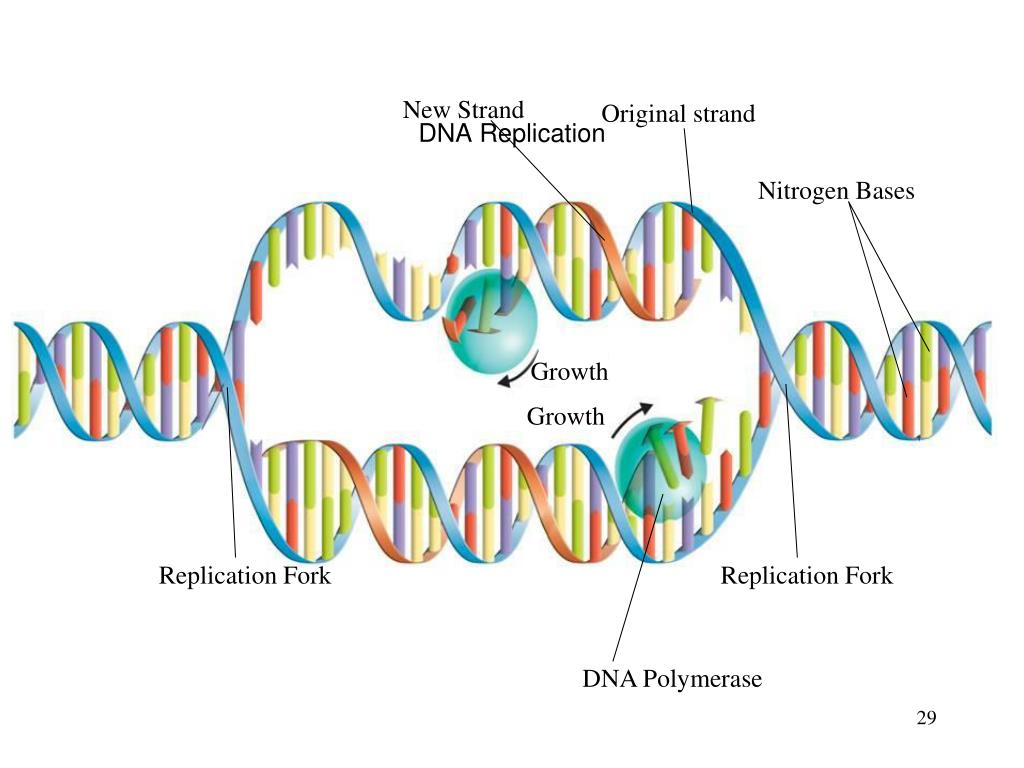
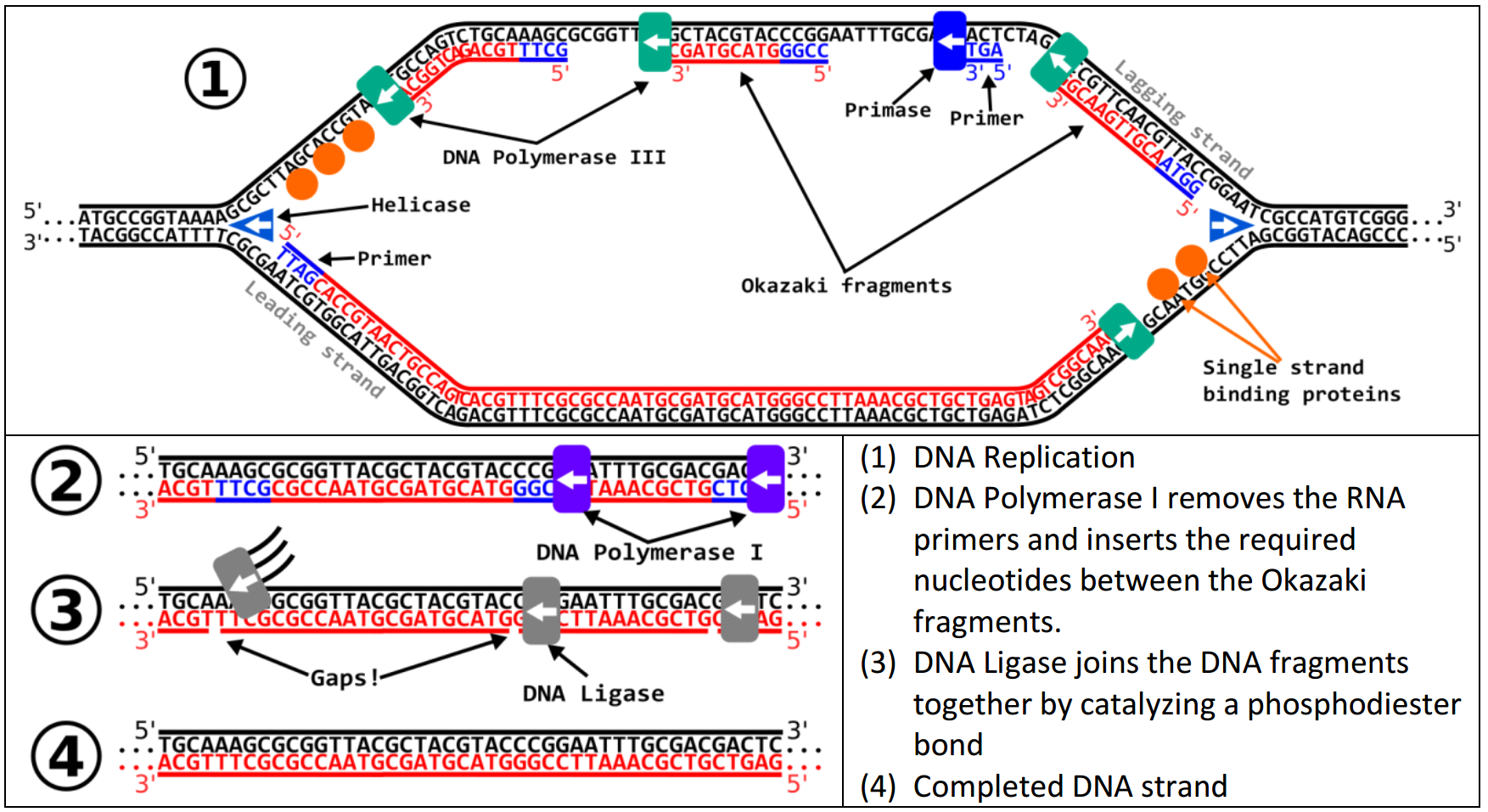
When two DNA copies are formed, they have an identical sequence of nucleotide bases and are divided equally into two daughter cells. This is known as semiconservative replication. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Gray indicates the original DNA strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized DNA.ĭuring DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Figure 2: The semiconservative model of DNA replication is shown. This model for replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied ( Figure 2). Figure 1: The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of bases in the other strand.īecause of the complementarity of the two strands, having one strand means that it is possible to recreate the other strand. For example, a strand of DNA with a nucleotide sequence of AGTCATGA will have a complementary strand with the sequence TCAGTACT ( Figure 1). This means that the two strands are complementary to each other. Answer: 2 on a question - Summarize the process of DNA replication and explain the significance of this process. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides, and cytosine with guanine, and that DNA is double stranded. The discovery and characterization of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA is copied. The replication of DNA occurs before the cell begins to divide into two separate cells. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication. DNA Ligase links Okazaki fragments to form a continuos strand.When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. Pol I excises RNA primer and fills the gap.ħ. Pol III elongates primer produces Okazaki fragmentĦ. Antipolar lagging strand primer synthesizes RNA primer.ĥ. Polymerase III (Pol I-IV) synthesizes the leading strand in the 5'-3' direction. Primase adds an RNA primer with an OH group to chemically bond with the first dNTP.Ĥ. Binding proteins keep strands separate and topoisomerase relieves tension and removes kinks to allow the double helix molecule to continue to unravel.ģ. Helicase separates antipolar strands forming a replication fork.Ģ. Each existing or old strand separated and served as a template for the synthesis of a new second strand so that each daughter DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one new strand, This is called semi-conservative replication and though other hypotheses were proposed experiments proved this hypothesis.ĭNA Replication Summary1. This step depends on the specific interaction of DNA. They suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the production of new strands, with bases being added to the new strands according to complimentary base-pairing rules. The initiation step of DNA replication is the crucial determinant of proliferation in all organisms.

Watson and Crick suggested that the A-T and C-G pairing rules suggested a way for DNA to be copied prior to mitosis or meiosis. The structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds that form between the bases called adenine and thymine and the bases guanine and cytosine. These two long strands twist around each other and certain of the nitrogenous bases pair inside the spiral forming a double helix molecule.
Summarize the process of dna replication series#
DNA is a long linear polymer that has two major components: a backbone made up of sugar and phosphate groups and a series of nitrogenous bases that project from the backbone. Watson and Crick developed a model for the secondary structure of DNA in 1953. Some teacher out there needs to answer this now


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
